Nearly lost to history
Tutankhamun was only the age of nine when he became king of Egypt during the 18th dynasty of the New Kingdom (c. 1332–1323 B.C.E.). His story would have been lost to history if it were not for the discovery of his tomb in 1922 by the archaeologist Howard Carter in the Valley of the Kings. His nearly intact tomb held a wealth of objects that give us unique insights into this period of ancient Egyptian history.
New Kingdom of the Egyptian Empire, c. 1500 B.C.E.
Tutankhamun ruled after the Amarna age, when the pharaoh Akhenaten, Tutankhamun’s probable father, turned the religious attention of the kingdom to the worship of the god Aten, the sun disc. Akhenaten moved his capital city to the site of Akhetaten (also known as Amarna), in Middle Egypt—far from the previous pharaoh’s capital. After Akhenaten’s death and the rule of a short-lived pharaoh, Smenkhkare, Tutankhamen shifted the focus of the country’s worship back to the god
and returned the religious center back to Thebes.
Tutankhamun married his half-sister, Ankhesenamun, but they did not produce an heir. This left the line of succession unclear. Tutankhamun died at the young age of eighteen, leading many scholars to speculate on the manner of his death—chariot accident, murder by blow to the head, and even a hippopotamus attack! The answer is still unclear. Tutankhamun’s much-older advisor (and possible step-grandfather), Ay, married the widowed Ankhesenamun and became pharaoh.
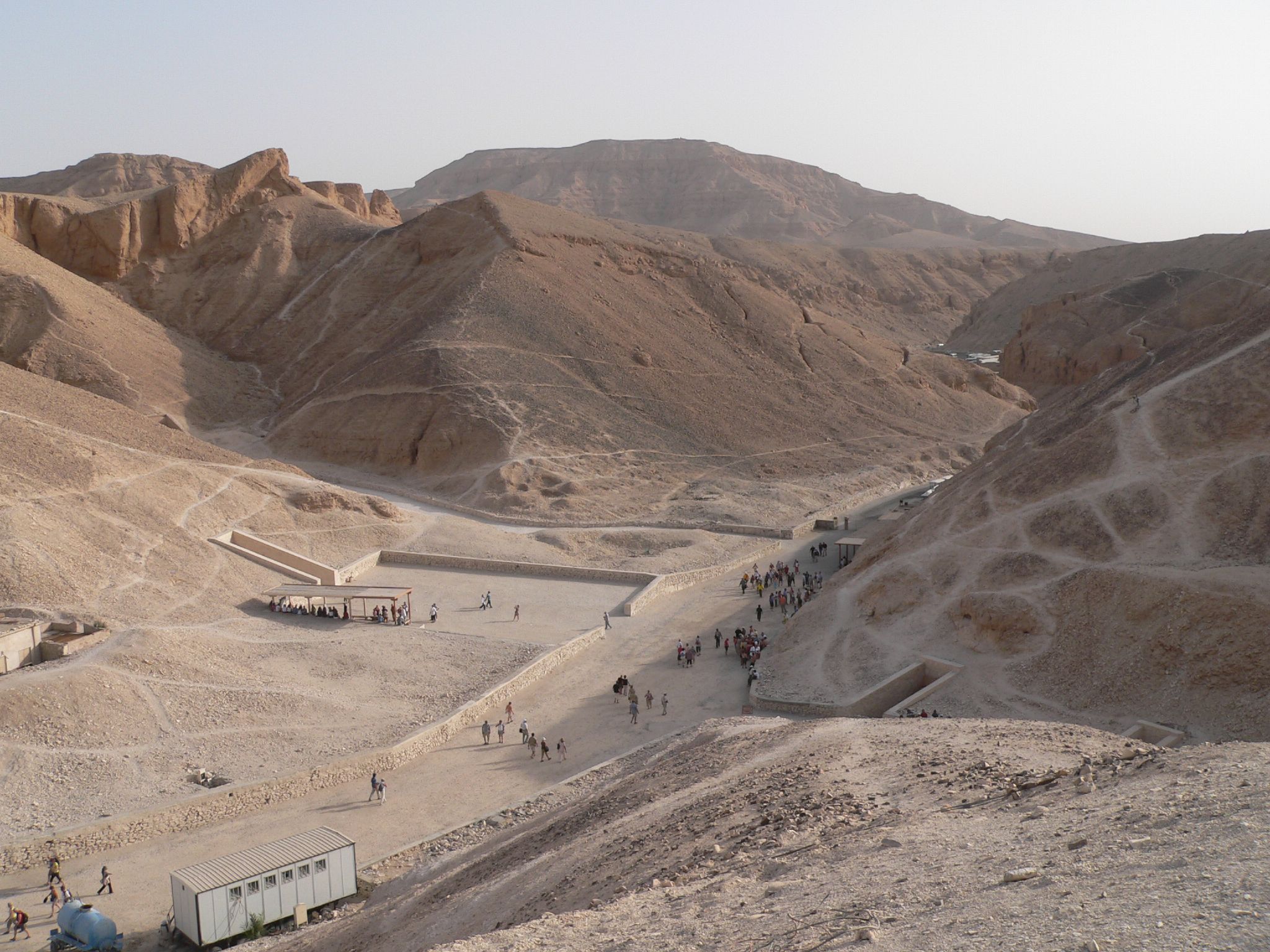
Valley of the Kings, Egypt (photo: Troels Myrup, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)
The tomb
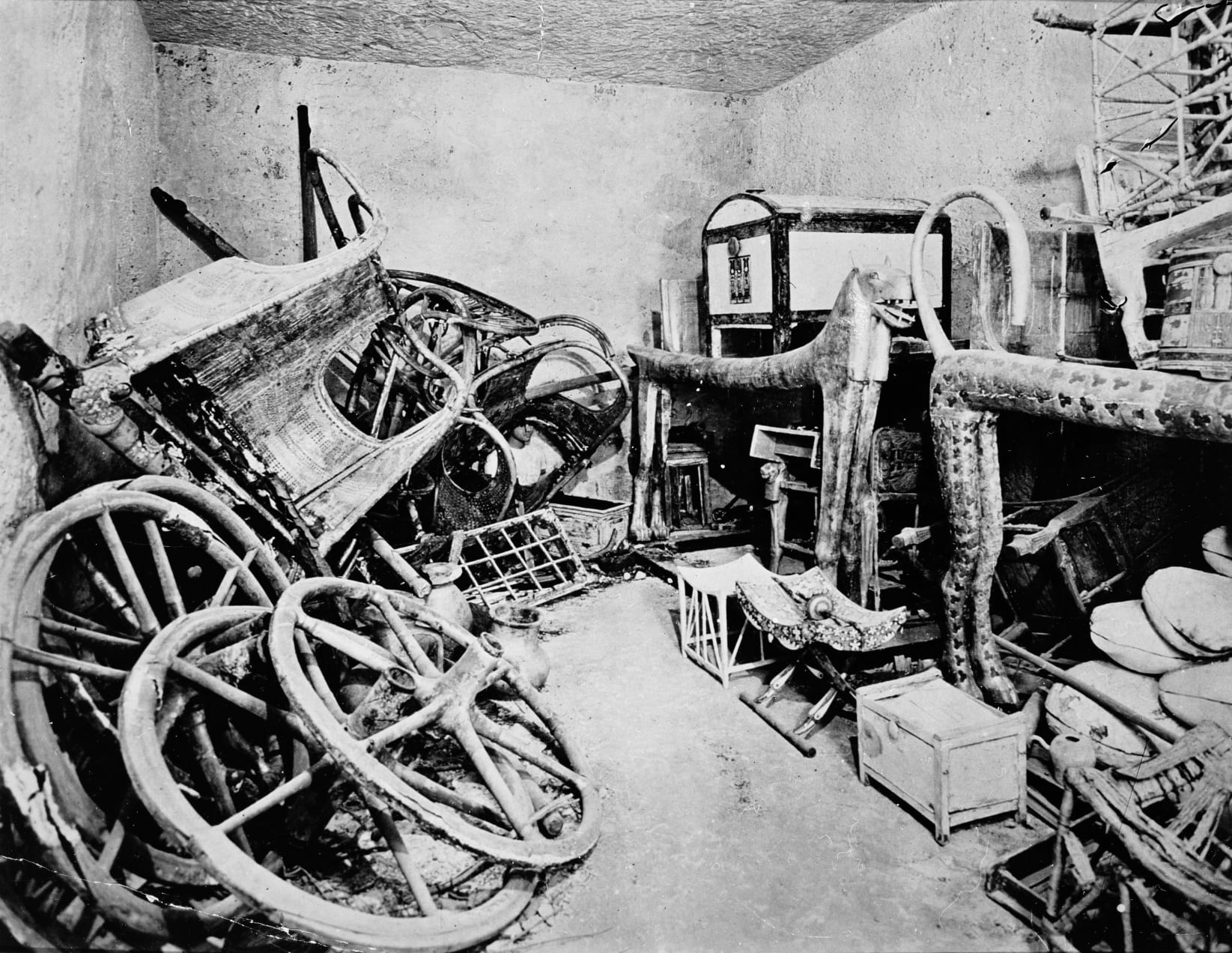
During the early twentieth century, Howard Carter, a British Egyptologist, excavated for many years in the Valley of the Kings—a royal burial ground located on the west bank of the ancient city of Thebes. He was running out of money to support his archaeological digs when he asked for funding for one more season from his financial backer, the fifth Earl of Carnarvon. Lord Carnarvon granted him one more year—and what a year it was!
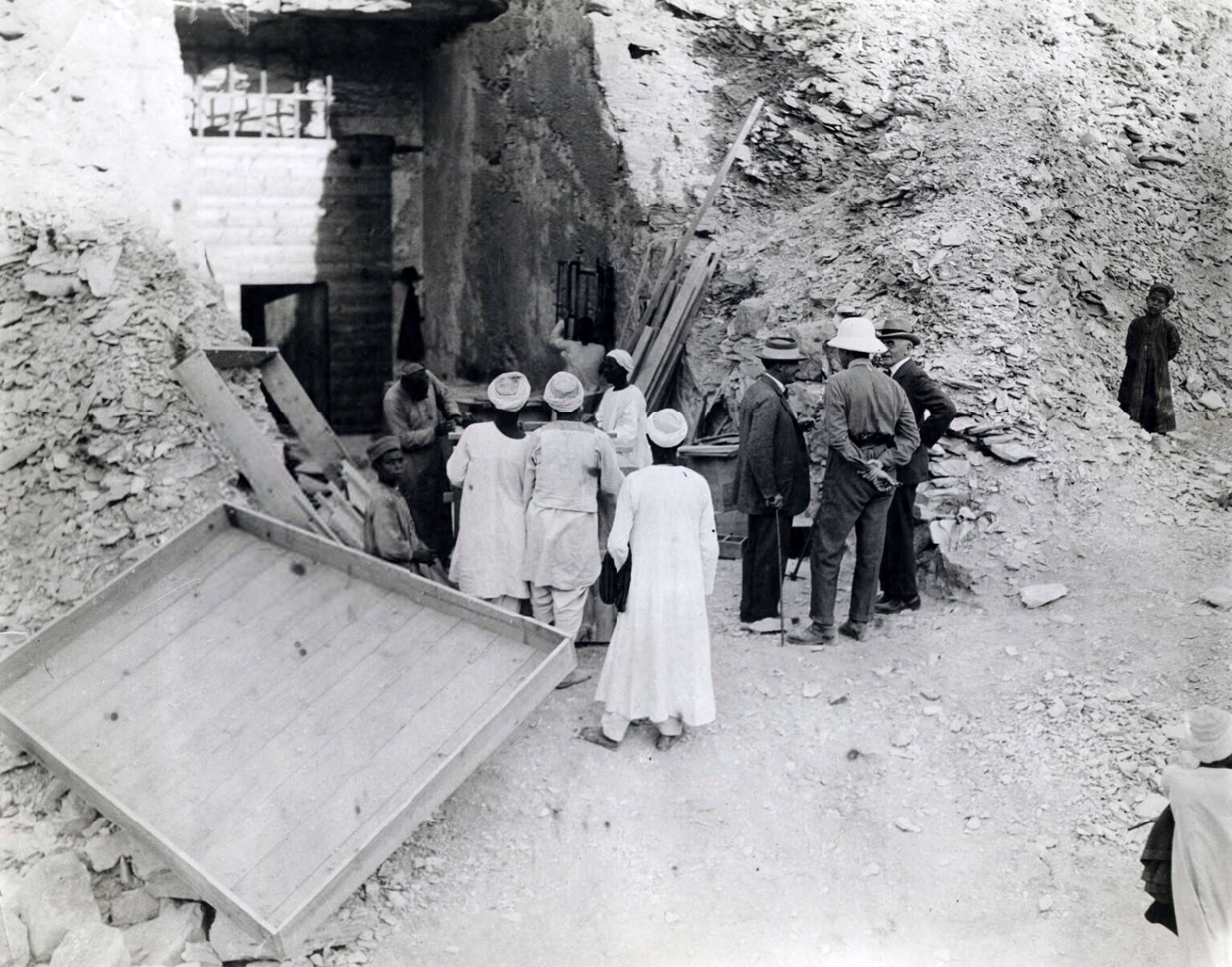
George Edward Stanhope Molyneux Herbert, Fifth Earl of Carnarvon, with Howard Carter during his initial visit to the tomb, 1922, 7 5/8 x 9 5/8 inches (National Portrait Gallery, London; photo: Keystone Press Agency Ltd.)
At the beginning of November 1922, Carter came upon the first of twelve steps of the entrance that led to the tomb of Tutankhamun. He quickly recovered the steps and sent a telegram to Carnarvon in England so they could open the tomb together. Carnarvon departed for Egypt immediately and on November 26, 1922, they made a hole in the entrance of the antechamber in order to look in. Carter states:
“At first I could see nothing, the hot air escaping from the chamber causing the candle flame to flicker, but presently, as my eyes grew accustomed to the lights, details of the room within emerged slowly from the mist, strange animals, statues, and gold—everywhere the glint of gold.” [1]
Harry Burton, View of tomb interior, 1922 (Tutankhamun Archive, Griffith Institute, University of Oxford)
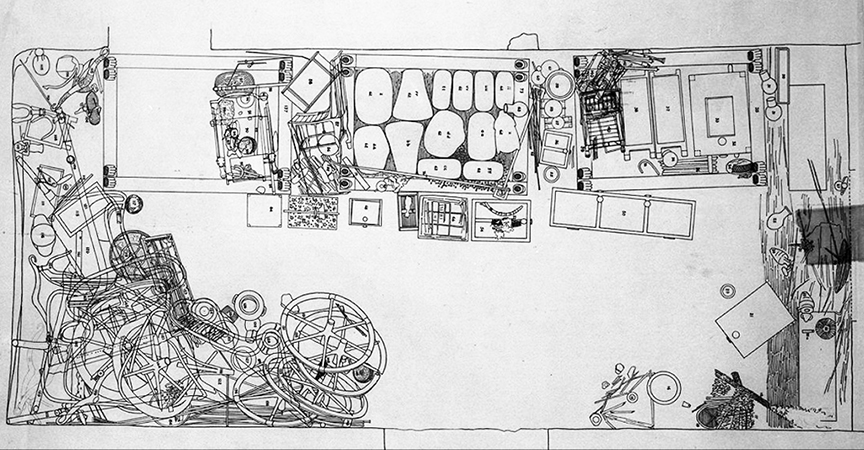
The task of cataloging the finds was an immense undertaking for the team. Carter spent a decade systematically recording the finds and having them photographed.
Howard Carter, Drawing of Tutankhamun’s tomb (Tutankhamun Archive, Griffith Institute, University of Oxford)
The innermost coffin
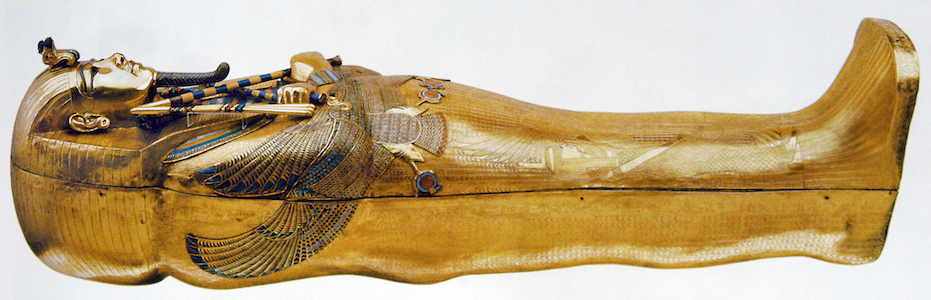
Tutankhamun’s sarcophagus (a box-like stone container) held not one but three coffins in which to hold the body of the king. The outer two coffins were crafted in wood and covered in gold along with many semiprecious stones, such as lapis lazuli and turquoise.
Tutankhamun’s tomb, innermost coffin, New Kingdom, 18th Dynasty, c. 1323 B.C.E., gold with inlay of enamel and semiprecious stones (Egyptian Museum, Cairo)
The inner coffin, however, was made of solid gold. When Howard Carter first came upon this coffin, it was not the shiny golden image we see in the Egyptian Museum today. In his excavation notes, Carter states, it was:
“covered with a thick black pitch-like layer which extended from the hands down to the ankles (top image). This was obviously an anointing liquid which had been poured over the coffin during the burial ceremony and in great quantity (some two buckets full).” [2]
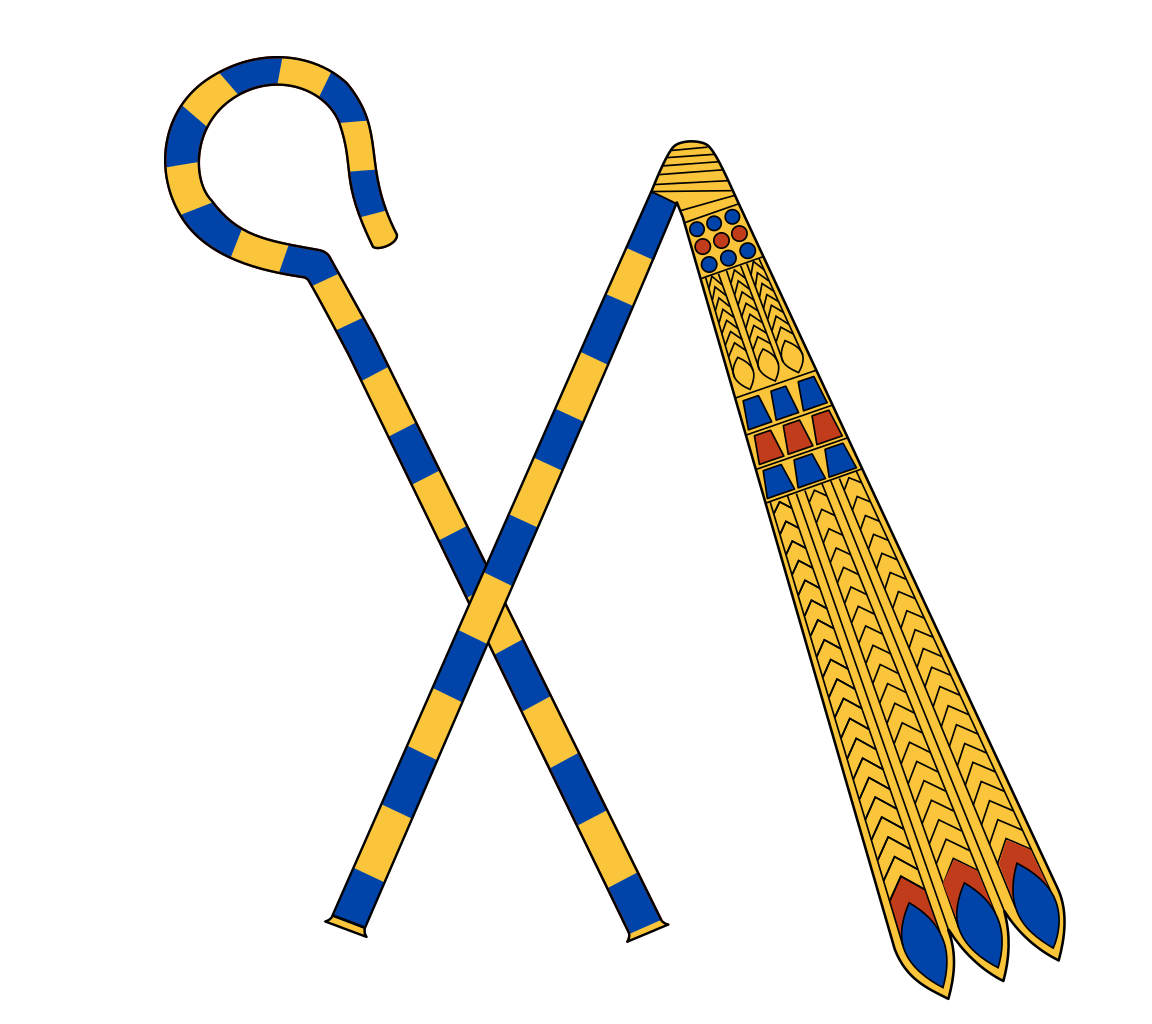
Egyptian crook and flail (by: Jeff Dahl, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The image of the pharaoh is that of a god. The gods were thought to have skin of gold, bones of silver, and hair of lapis lazuli—so the king is shown here in his divine form in the afterlife. He holds the crook and flail, symbols of the king’s right to rule. The goddesses and, inlaid with semiprecious stones, stretch their wings across his torso. Beneath these goddesses are two more— and —etched into the gold lid.
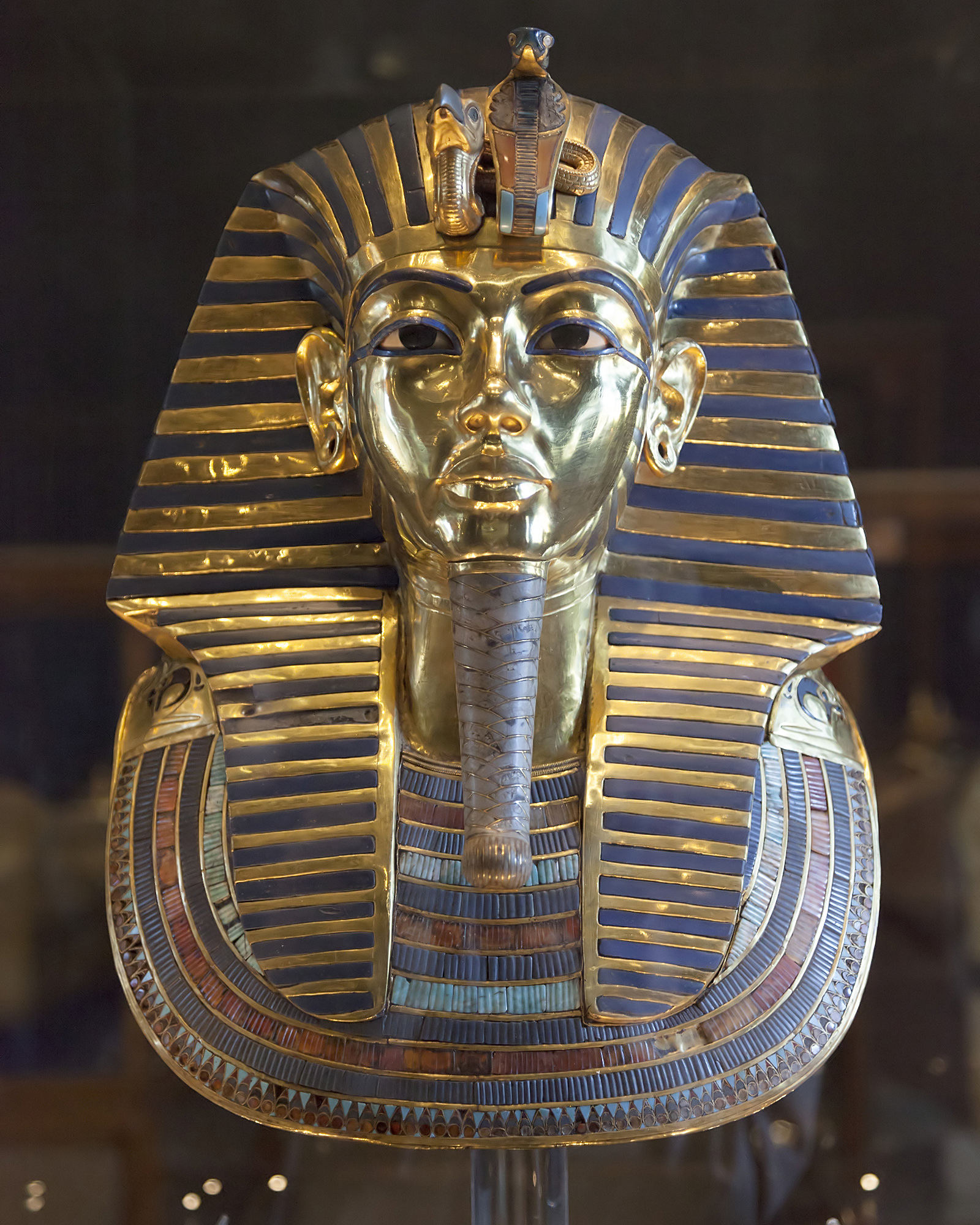
Death Mask from innermost coffin, Tutankhamun’s tomb, New Kingdom, 18th Dynasty, c. 1323 B.C.E., gold with inlay of enamel and semiprecious stones (Egyptian Museum, Cairo) (photo: Roland Unger, CC BY-SA 3.0)
The death mask of Tutankhamun
The death mask is considered one of the masterpieces of Egyptian art. It originally rested directly on the shoulders of the mummy inside the innermost gold coffin. It is constructed of two sheets of gold that were hammered together and weighs 22.5 pounds (10.23 kg). Tutankhamen is depicted wearing the striped nemes headdress (the striped head-cloth typically worn by pharaohs in ancient Egypt) with the goddesses Nekhbet and Wadjet depicted again protecting his brow. He also wears a false beard that further connects him to the image of a god as with the inner coffin. He wears a broad collar, which ends in terminals shaped as falcon heads. The back of the mask is covered with Spell 151b from the Book of the Dead, which the Egyptians used as a road map for the afterlife. This particular spell protects the various limbs of Tutankhamun as he moves into the underworld.